Professional Guide: Optimal Mounting Height and Spacing for LED High Bay Lights
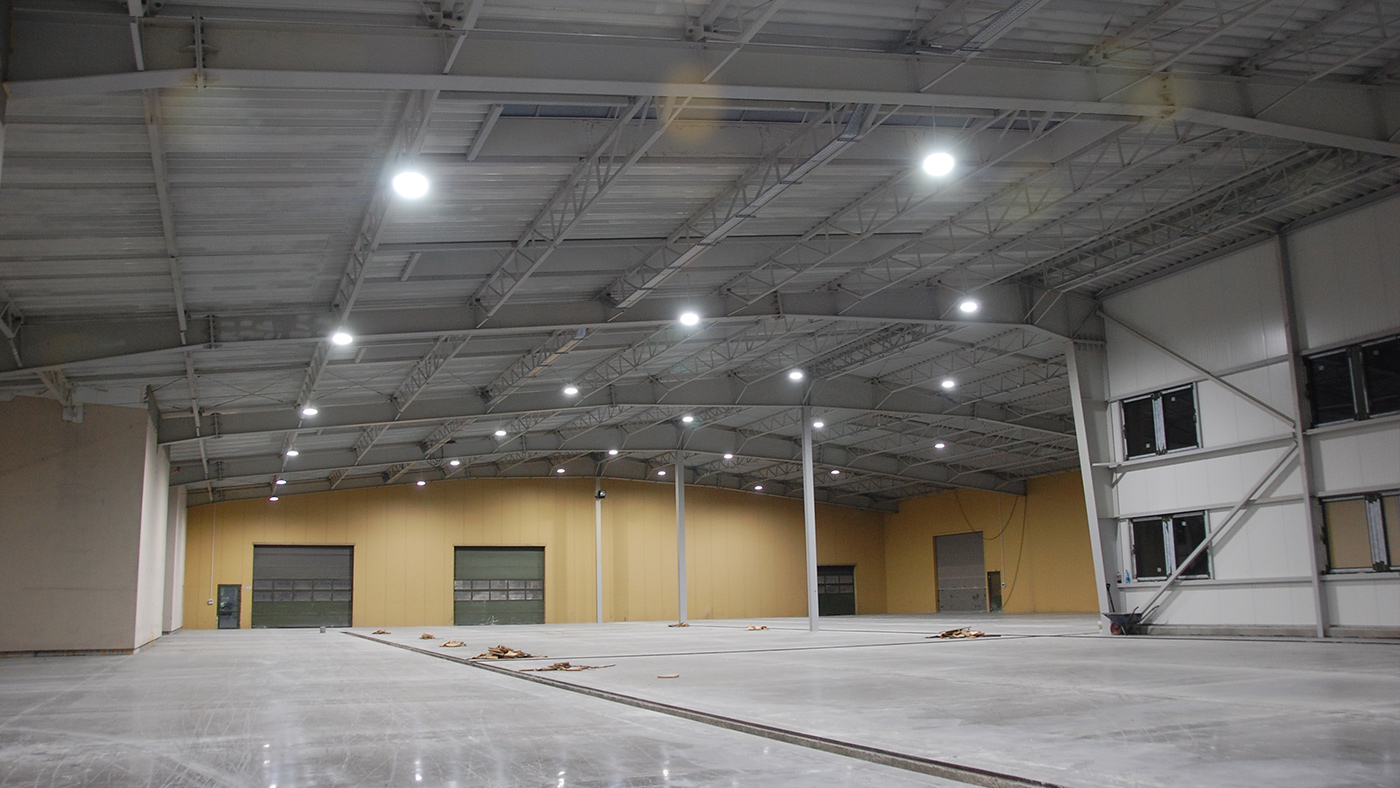
LED High Bay Lights are designed to deliver high-intensity, uniform illumination in large indoor or semi-indoor spaces such as warehouses, manufacturing plants, gymnasiums, supermarkets, and exhibition halls. To achieve maximum lighting efficiency, proper installation height and fixture spacing are critical. These two parameters directly influence light distribution, brightness uniformity, and energy efficiency.
1. Understanding Mounting Height
The mounting height refers to the vertical distance between the light fixture and the working surface (or floor). LED High Bay Lights typically operate effectively at 8–30 meters (26–98 feet), depending on the wattage, beam angle, and application requirements.
General guidelines for mounting height:
-
Low-bay applications (6–8 meters / 20–26 ft): Use lower wattage fixtures (e.g., 100W–150W) with wider beam angles (90°–120°) to cover a larger area while preventing excessive glare. Suitable for assembly workshops, small warehouses, or retail spaces.
-
Medium-bay applications (8–12 meters / 26–39 ft): Use medium power fixtures (e.g., 150W–200W) with beam angles between 90°–120°, depending on required lux levels. This range is common in general warehouses, production areas, and logistics centers.
-
High-bay applications (12–18 meters / 39–59 ft): Use higher wattage fixtures (200W–300W) with narrower beam angles (60°–90°) to focus light and maintain adequate lux at floor level. Ideal for large distribution centers, sports facilities, or aircraft hangars.
-
Ultra-high installations (18–30 meters / 59–98 ft): Specialized high-output fixtures (e.g., 300W–500W) with beam angles of 30°–60° are used for extremely tall spaces such as stadiums, shipyards, or mining facilities.
Why height matters:
-
Too low: Causes excessive glare, uneven distribution, and wasted energy due to overlapping beams.
-
Too high: Results in insufficient lux levels on the floor, creating dim spots and reducing visibility for tasks.
2. Determining Optimal Spacing
The spacing between fixtures depends on beam angle, mounting height, and required uniformity. Proper spacing ensures overlapping light patterns that eliminate dark areas while avoiding over-illumination.
Common engineering rule:
-
Spacing-to-Mounting Height Ratio (S/MH) is typically 1.0–1.5.
-
Example: At a mounting height of 12 meters, spacing should be between 12–18 meters.
-
-
Narrow beam (30°–60°): Closer spacing (S/MH ≈ 1.0–1.2) for higher lux and concentrated light.
-
Wide beam (90°–120°): Wider spacing (S/MH ≈ 1.3–1.5) for general illumination.
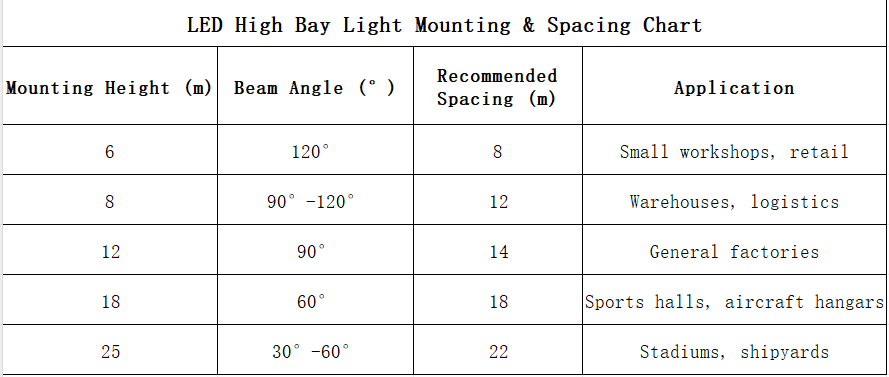
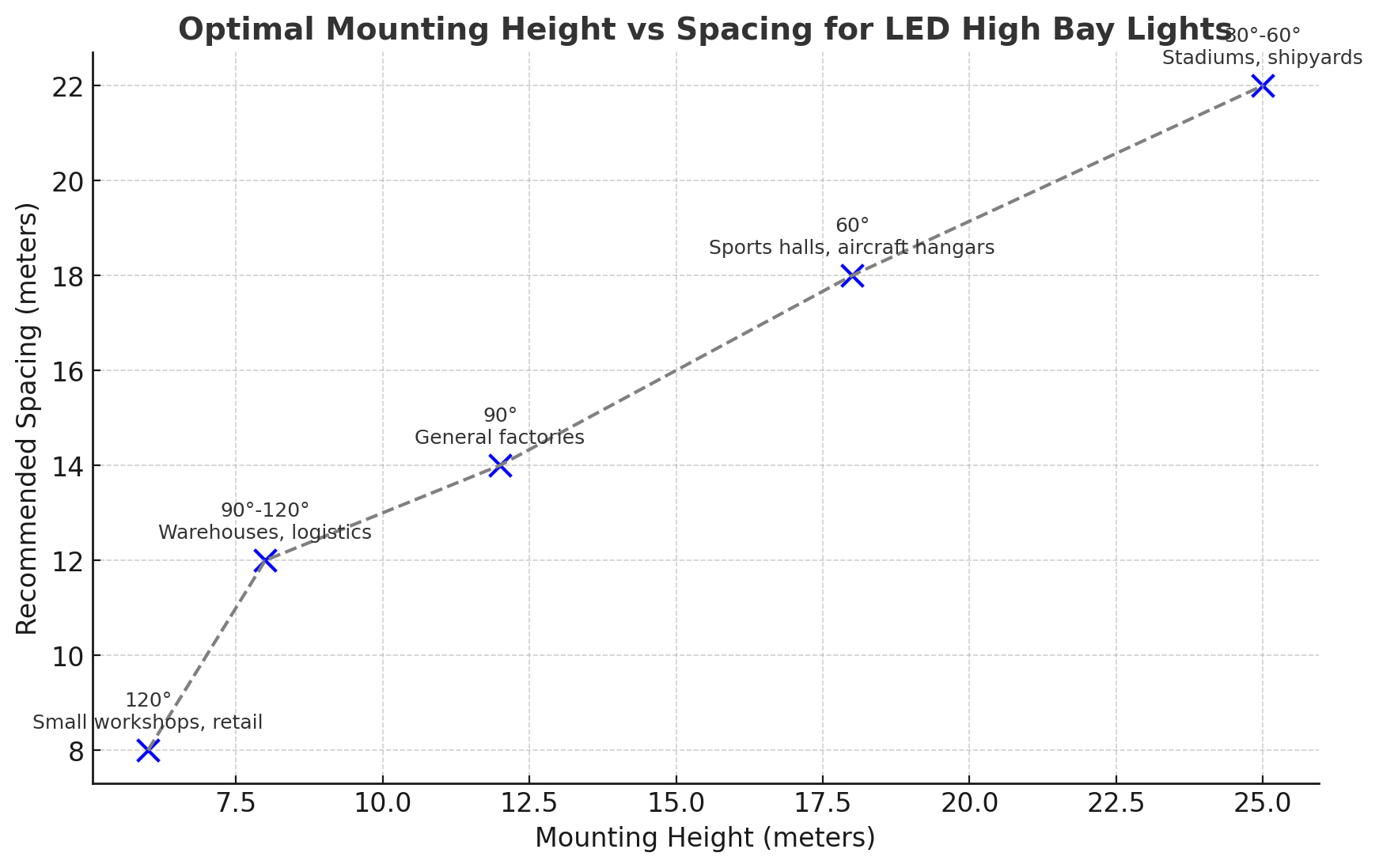
Example configurations:
| Mounting Height | Beam Angle | Recommended Spacing | Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| 6–8 m | 120° | 8–10 m | Small workshops, retail |
| 8–12 m | 90°–120° | 10–15 m | Warehouses, logistics |
| 12–18 m | 60°–90° | 12–18 m | Large factories, sports halls |
| 18–30 m | 30°–60° | 18–25 m | Stadiums, shipyards |
3. Lux Level and Task Requirements
The recommended lux level varies by application:
-
General storage: 100–200 lux
-
Assembly work: 300–500 lux
-
Precision machining: 500–1000 lux
-
Sports facilities: 300–750 lux
To achieve these targets, engineers adjust height and spacing in combination with fixture wattage, beam angle, and lumen output.
4. Practical Engineering Tips
-
Use photometric analysis (IES files) to simulate light distribution before installation.
-
Consider reflectance of walls, ceilings, and floors; darker surfaces require higher lumen output.
-
Avoid shadowing caused by overhead cranes or tall racks; adjust fixture positions accordingly.
-
Include maintenance clearance for safe fixture replacement or cleaning.
-
Integrate smart controls (motion sensors, daylight harvesting) to maximize energy savings.
5. Example Case Study
A warehouse with a 12-meter ceiling height requires 200 lux average illumination:
-
Fixture: 200W LED High Bay, 90° beam, 32,000 lumens
-
Mounting height: 12 m
-
Spacing: 14 m between fixtures
-
Layout: 6 rows × 10 fixtures
Result: Even light coverage with 0.8 uniformity, meeting the lux requirement with energy efficiency.
Conclusion
For LED High Bay Lights, optimal mounting height and spacing are determined by balancing light distribution, lux requirements, and energy use. Following the 1.0–1.5 S/MH ratio and adjusting for beam angle ensures even coverage without wasted power. Always verify with lighting simulations to achieve professional, application-specific results.


